
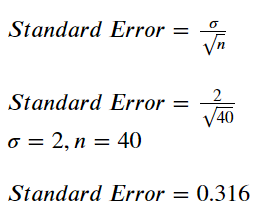
In this article, we will discuss what is the standard error in statistics, standard error equation, standard error of estimate formula, what is the standard error of mean, standard error of mean formula etc. The standard error makes use of sample data whereas standard deviation makes use of population data. Although both the standard deviation and standard error are similar, there is one important difference between them.

The larger the number, the more the data is spread. A small standard error implies that the population is in a uniform shape.Īs we know standard error is quite similar to the standard deviation as both measures the amount of data is spread. A large standard error indicates that there are various changes in the population. It tells the way sample means determine the true population means. The standard error is an important statistical measure and it is related to the standard deviation. In order to know the way a sample is denoting the population, we are required to measure the standard error for the particular measurement. There are multiple ways to define a population and we should be through about the definition of population. A population is a whole group from which the data has been gathered. For example, the sample may be the data collected about the height of the student in the class. However, please note that the student’s t-test is applicable for data set with a sample size of less than 30.In statistics, the sample refers to the data which is gathered for the particular group. This test is run to check the validity of a null hypothesis based on the critical value at a given confidence interval and degree of freedom. It is imperative for a statistician to understand the concept of t-test as it holds significant importance while drawing conclusive evidence about whether or not two data sets have statistics that are not very different. T = ( x̄ 1 – x̄ 2) / √ Relevance and Use of t-Test Formula Step 4: Finally, the formula for a two-sample t-test can be derived using observed sample means (step 1), sample standard deviations (step 2) and sample sizes (step 3) as shown below. Step 3: Next, determine the size of the two samples, which are denoted by and. Step 2: Next, determine the standard deviation of the two samples, which are denoted by and. Step 1: Firstly, determine the observed sample mean of the two samples under consideration. The formula for the two-sample t-test can be derived by using the following steps: Step 4: Finally, the formula for a one-sample t-test can be derived using the observed sample mean (step 1), the theoretical population means (step 1), sample standard deviation (step 2) and sample size (step 3), as shown below. Step 3: Next, determine the sample size, which is the number of data points in the sample.

Step 2: Next, determine the standard deviation of the sample, and it is denoted by s. The sample mean and population mean is denoted by and μ, respectively. Step 1: Firstly, determine the observed sample mean, and the theoretical population means specified. The formula for one-sample t-test can be derived by using the following steps: So, the hypothesis that the statistics of the two samples are significantly different can’t be rejected. Therefore, the absolute t-test value is 4.31, which is greater than the critical value (3.03) at a 99.5% confidence interval with a degree of freedom of 30. T-Test value is calculated using the formula given below Determine if the sample’s statistics are different at a 99.5% confidence interval. The two samples have means of 10 and 12, standard deviations of 1.2 and 1.4, and sample sizes of 17 and 15. Let us take the example of two samples to illustrate the concept of a two-sample t-test.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
